Industry information
Company News
- Aluminum veneer customization: the art of creating personalized spaces
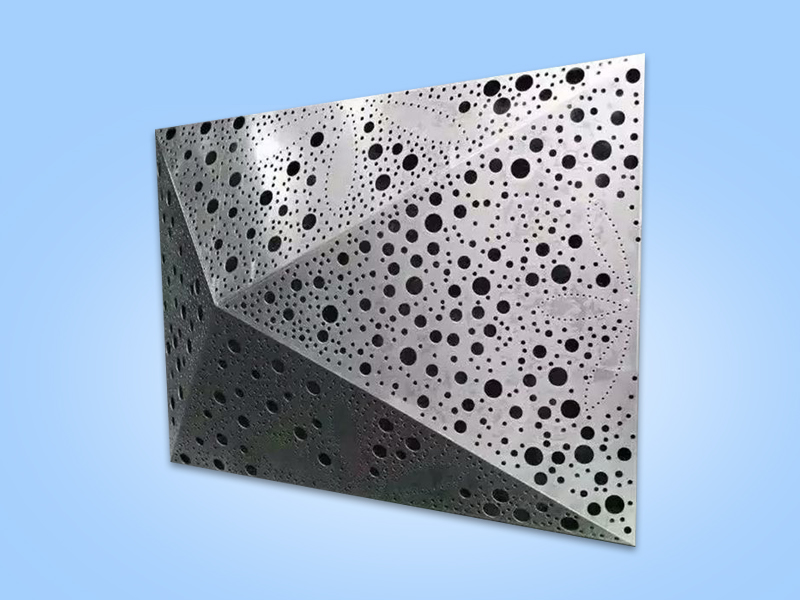
- New gameplay of aluminum veneer: punching art, fully showcasing individual charm
- Fluorocarbon aluminum veneer: a new favorite in architecture, combining beauty and durability
- Aluminum veneer: not only a building material, but also a carrier of art
- Fluorocarbon aluminum veneer: the fashionable "outerwear" of the construction industry
Industry dynamics
- Personalized customization, new trend of aluminum veneer
- Aluminum veneer customization, creating personalized space and new fashion
- Professional customization of aluminum veneer ceiling to meet personalized needs
- The future development trend of bold innovation hollow carved aluminum veneer curtain wall
- Aluminum veneer is not just a board, it can also create an artistic sense!
Frequently asked questions
- Is the production process of aluminum veneer environmentally friendly?
- What is the seismic performance of aluminum veneer in building exterior design?
- How does aluminum veneer provide the weather resistance required for modern buildings?
- What is the antioxidant performance of aluminum veneer?
- Is there any restriction on the size customization of aluminum veneer?
contact us
Mobile:+86 15627778610
Email: 2201229786@qq.com
Address: No. 5 Binjiang Road, High tech Zone, Zhaoqing City, Guangdong Province
Application of aluminum veneer in low-carbon buildings
- Author: Jinba Aluminum Industry (Guangdong) Co., Ltd
- Release time: March 17, 2025 23:14:25
- Click:0

With the global emphasis on environmental protection and low-carbon buildings,Aluminum veneerAs a new type of building material, its application in low-carbon buildings is becoming increasingly widespread. Aluminum veneer has the advantages of lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, which can effectively reduce the energy consumption and carbon emissions of buildings, achieving the goal of low-carbon environmental protection. Below, we will provide a detailed introduction to the application of aluminum veneer in low-carbon buildings.
1、 Improve energy utilization efficiency
Aluminum veneer has excellent thermal insulation and thermal insulation properties, which can effectively reduce the energy consumption and carbon emissions of buildings. For example, using aluminum veneer for exterior wall insulation in winter can effectively reduce the energy required for indoor temperature drop, thereby reducing heating energy consumption; Using aluminum veneer for exterior wall shading in summer can effectively reduce the energy required for indoor temperature rise, thereby reducing air conditioning energy consumption. Aluminum veneer can also be used for insulation treatment of roofs and windows, further improving energy efficiency.
2、 Reduce carbon emissions
The production process of aluminum veneer has lower carbon emissions compared to traditional building materials, so using aluminum veneer in low-carbon buildings can effectively reduce the carbon emissions of buildings. Aluminum veneer has a long service life and can reduce carbon emissions during building replacement and maintenance.
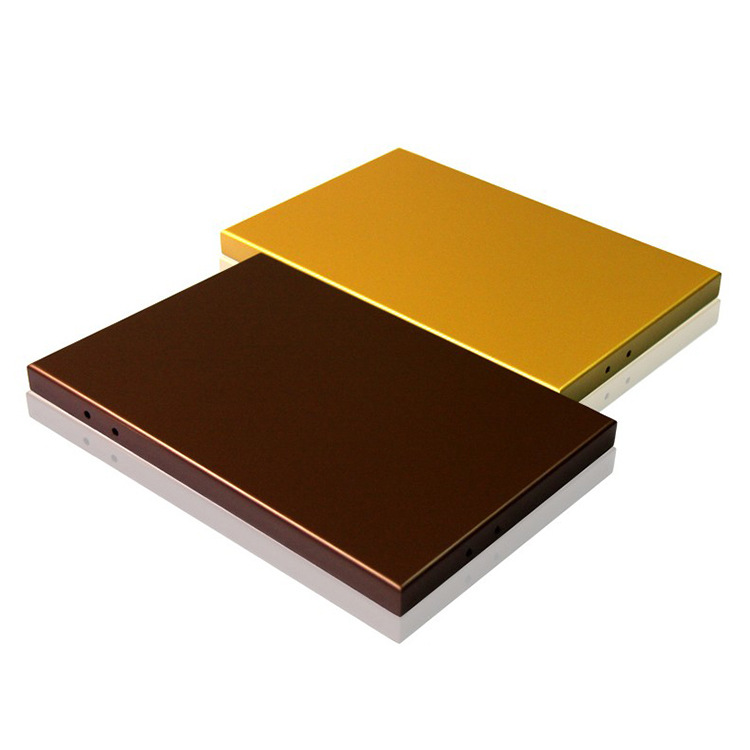
3、 Improve the aesthetics and comfort of buildings
Aluminum veneer has good decorative and malleable properties, and can be customized according to different design requirements to achieve the best decorative effect. Aluminum veneer also has good breathability and waterproof performance, which can improve the comfort and user experience of buildings.
4、 Promote sustainable development
As a renewable resource, the production process of aluminum veneer has lower environmental impact and resource consumption compared to traditional building materials. The use of aluminum veneer in low-carbon buildings can promote sustainable development, protect the environment and natural resources.
Aluminum veneer has broad application prospects and advantages in low-carbon buildings. In practical applications, it is necessary to select and use according to the actual situation and design requirements to achieve the best decorative effect and energy-saving and emission reduction effect.





 Customer service QQ
Customer service QQ